TL;DR
- Why vector similarity alone misses relationship-based queries
- GraphRAG-lite: practical knowledge graphs without enterprise complexity
- Entity resolution, graph hops, and hybrid vector+graph retrieval
Vector similarity answers: "What's semantically close?"
GraphRAG answers: "What's connected?"
Different questions. Different answers. Both valuable.
SemanticStudio implements GraphRAG-lite—a practical knowledge graph approach that complements vector retrieval without the complexity of full-scale graph databases.
The Limits of Pure Vector RAG
Vector retrieval is powerful:
Query: "What are our Q4 revenue numbers?"
Vector RAG: Retrieves Q4 financial documents (high semantic similarity)
But it has blind spots:
Query: "Who worked with Customer X on Project Y?"
Vector RAG: Returns documents mentioning Customer X or Project Y
BUT misses the connection between them
Vector similarity finds related content. It doesn't find relationships.
GraphRAG: Relationship-Aware Retrieval
GraphRAG adds a knowledge graph layer:
Query: "Who worked with Customer X on Project Y?"
GraphRAG:
1. Find Customer X node
2. Traverse to Project Y (1 hop)
3. Find People connected to that project
4. Return relationship-aware results
The graph captures what vectors miss.
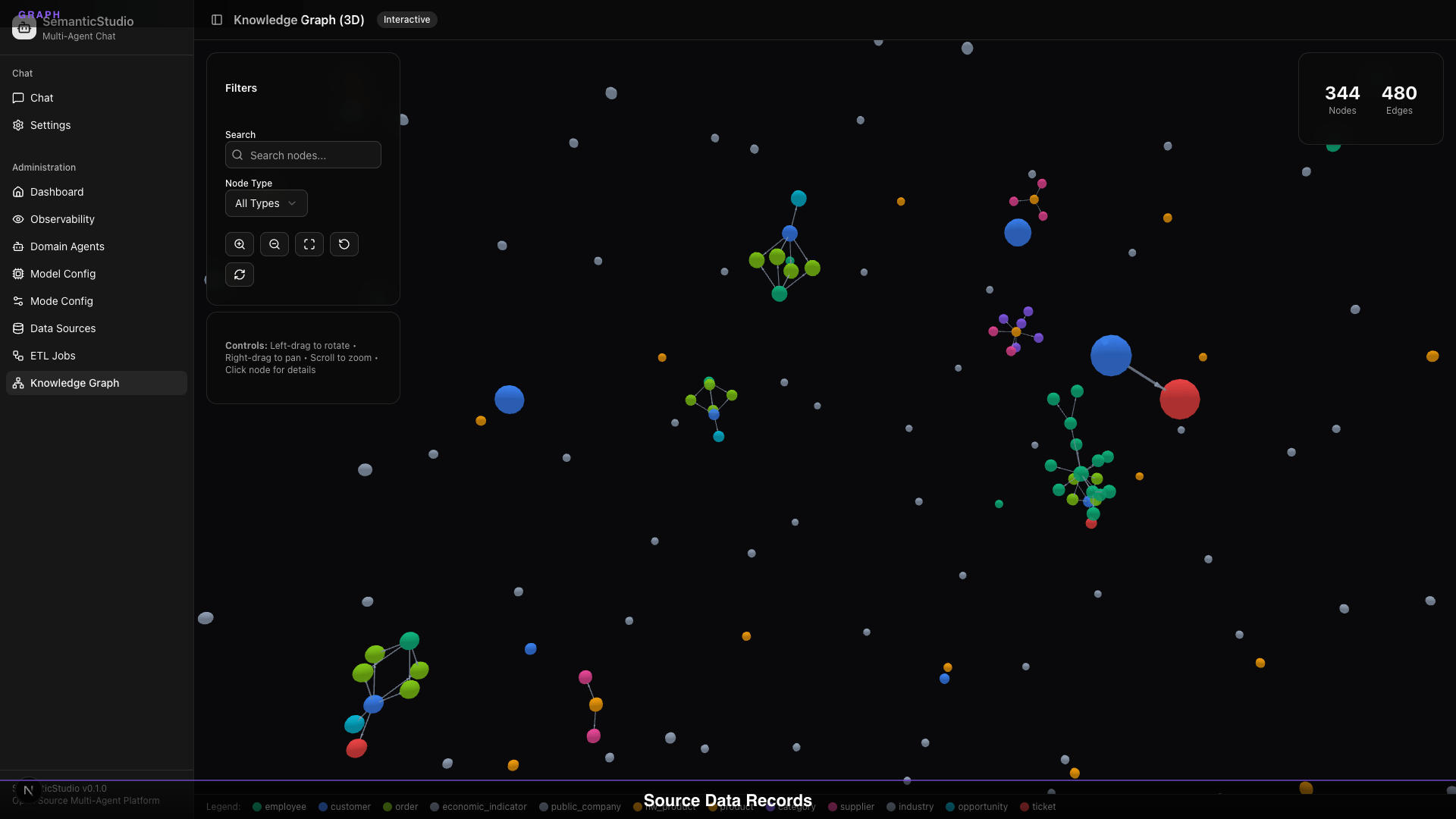
SemanticStudio's Knowledge Graph
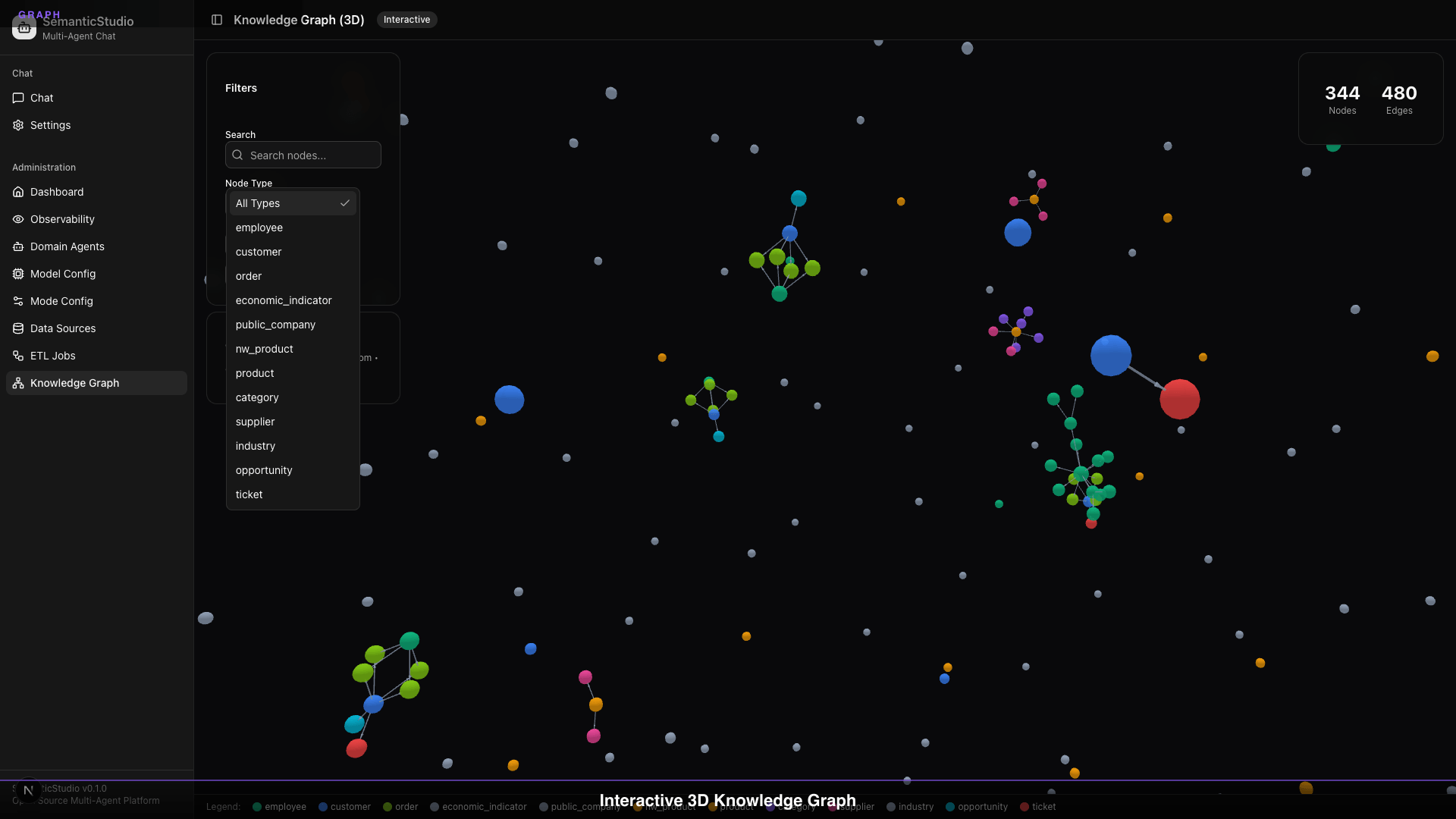
The visualization shows:
- 344 nodes: Entities extracted from your data
- 320 edges: Relationships between entities
- Color-coded: Different entity types (employee, product, customer, etc.)
- Interactive: Click, zoom, rotate, filter
Entity Types
SemanticStudio extracts and links multiple entity types:
| Entity Type | Color | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Employee | Blue | People in your organization |
| Product | Green | Products, services, offerings |
| Customer | Orange | Customer accounts |
| Industry | Yellow | Industry classifications |
| Category | Purple | Product categories |
| Order | Teal | Transaction records |
| Ticket | Pink | Support tickets |
| Economic Indicator | Gray | Market data |
Relationship Types
Entities connect through relationships:
PLACED_ORDER: Customer → OrderPROCESSED: Employee → OrderREPORTS_TO: Employee → EmployeeSUPPLIED_BY: Product → SupplierBELONGS_TO: Product → Category
Graph Hops by Mode
The depth of graph traversal varies by mode:
| Mode | Graph Hops | What It Finds |
|---|---|---|
| Quick | 0 | Entity match only |
| Think | 1 | Direct relationships |
| Deep | 2 | Second-degree connections |
| Research | 3 | Full exploration |
0 Hops (Quick Mode)
Query: "Tell me about Customer ABC"
→ Returns: Customer ABC node data only
1 Hop (Think Mode)
Query: "Tell me about Customer ABC"
→ Returns: Customer ABC + directly connected entities
(orders, assigned employees, products purchased)
2 Hops (Deep Mode)
Query: "Tell me about Customer ABC"
→ Returns: Customer ABC + connected entities +
their connections (employee teams, product categories,
related customers)
3 Hops (Research Mode)
Query: "Tell me about Customer ABC"
→ Returns: Full network exploration
(industry trends, supplier chains, market patterns)
Entity Resolution
Before building the graph, we need to resolve entities—identifying when different mentions refer to the same thing.
The Challenge
Your data might contain:
- "John Smith" (CRM record)
- "J. Smith" (email)
- "jsmith@company.com" (system log)
- Employee ID 12345 (database)
All the same person.
How SemanticStudio Resolves
- Extract mentions: Find entity references in text
- Normalize: Standardize format
- Match: Compare against known entities
- Link: Create canonical entity with aliases
The Semantic Layer
The semantic layer maps:
- Source tables to entity types
- Columns to entity properties
- Foreign keys to relationships
This creates a clean entity model from messy source data.
Exploring the Graph
SemanticStudio's graph explorer lets you:
Filter by Node Type
Focus on specific entity types:
- View only customers
- View only products
- View only employees
Click Nodes for Details
Click any node to see:
- Entity properties
- Connected nodes
- Relationship types
- Source records
Explore Connections

Trace relationships through the network:
- Follow edges between nodes
- Discover unexpected connections
- Visualize data relationships
View Source Records
See the underlying data:
- Source table
- Raw record data
- Last updated timestamp
Hybrid Retrieval
SemanticStudio doesn't replace vector RAG—it augments it:
Query Processing:
1. Vector search → Top-K semantically similar chunks
2. Entity extraction → Identify mentioned entities
3. Graph traversal → Expand with connected entities
4. Merge results → Combine and deduplicate
5. Context assembly → Build coherent context
When Vector Wins
- General semantic queries
- Topic-based retrieval
- Content similarity
When Graph Wins
- Relationship queries
- "Who worked with..."
- "What connects X and Y?"
- Network exploration
Best Together
Most queries benefit from both:
Query: "How is Customer ABC performing and who manages the relationship?"
Vector: Retrieves customer performance documents
Graph: Finds Customer ABC → linked to Employee (account manager)
→ Employee's recent interactions
Combined: Performance data + relationship context
Context Graph: The Memory Bridge
The knowledge graph stores business data. But how does your conversation connect to it?
That's where the Context Graph comes in—Tier 4 of the memory system. It bridges your personal conversation context to the domain knowledge graph.
How It Works
When you discuss or query entities:
User: "What's the churn risk for Acme Corp?"
↓
Context Graph: Creates reference
- User: you
- Entity: Acme Corp (customer node)
- Type: "queried"
- Context: "Asked about churn risk"
Now the system knows you've engaged with this entity.
Query Your History
Later, you can ask:
User: "What did I discuss about Acme Corp?"
↓
Context Graph: Lookup
- Find all your references to Acme Corp
- Return conversation context where it appeared
- Include relationship type (discussed, queried, mentioned)
Response: "You queried churn risk for Acme Corp in your
Q4 customer analysis session. We found they
had a 23% growth rate but elevated support
ticket volume..."
Privacy Isolation
Your context references are private:
- Each user's links are isolated
- Admins cannot see which entities you've discussed
- No cross-user data leakage
The Context Graph enables personalized, entity-aware memory while maintaining privacy.
Building the Knowledge Graph
The graph is built during ETL (covered in Part 7):
- Data ingestion: Load source data
- Entity extraction: Identify entities in content
- Relationship inference: Detect relationships
- Graph population: Build node and edge structure
- Incremental updates: Add new entities as data arrives
Graph Statistics
The ETL jobs page shows graph health:
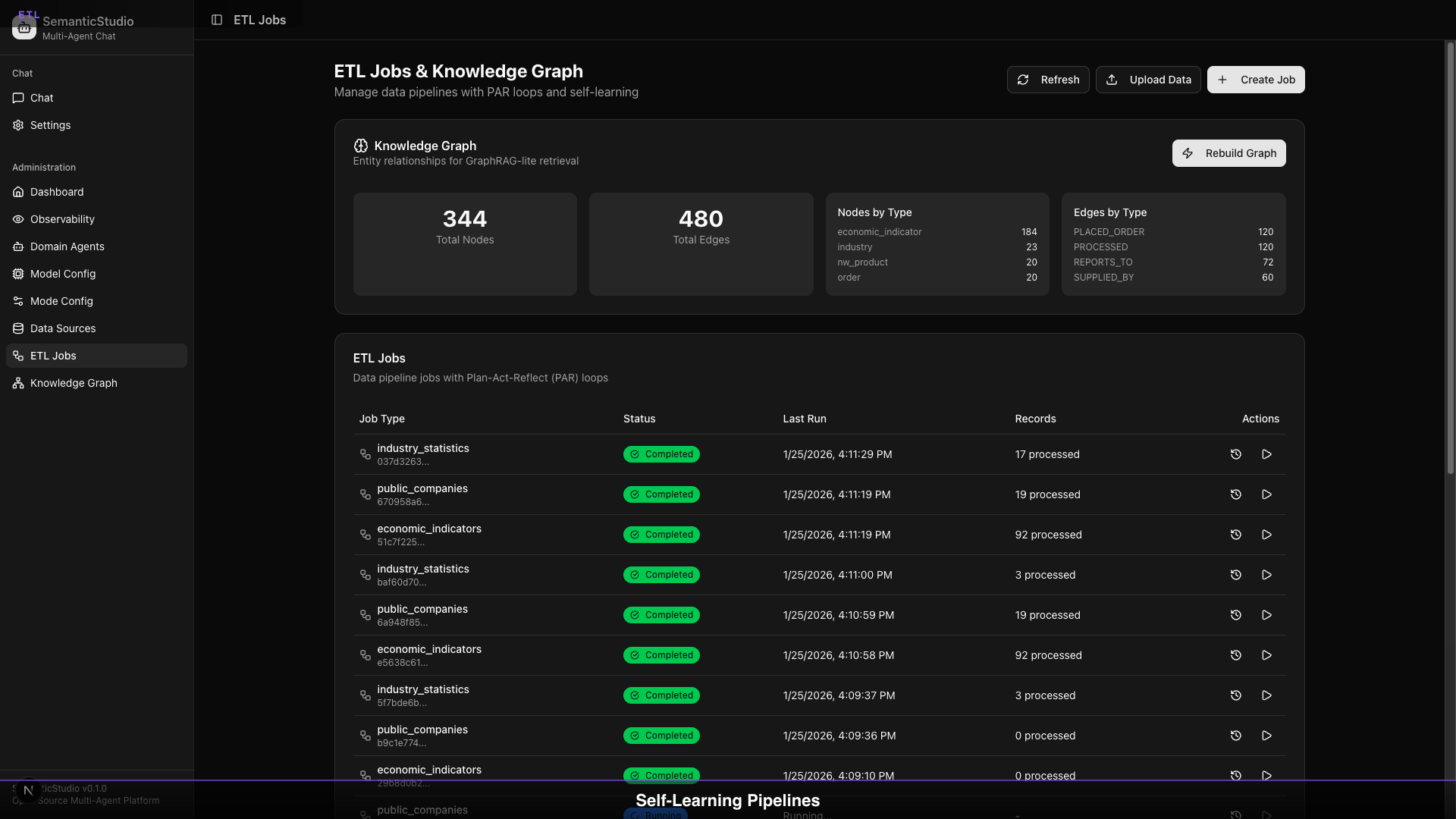
- Total Nodes: 344
- Total Edges: 320
- Nodes by Type: Distribution across entity types
- Edges by Type: Distribution across relationship types
Rebuilding the Graph
When you add significant new data:
- Click "Rebuild Graph"
- Full re-extraction runs
- Relationships are re-inferred
- Graph is regenerated
Incremental updates happen automatically; full rebuilds are manual.
When to Use GraphRAG
Enable GraphRAG when:
- Your data has meaningful relationships
- Users ask "who/what/how connected" questions
- Entity resolution matters
- Network effects exist in your domain
Skip GraphRAG when:
- Simple document retrieval suffices
- No meaningful relationships exist
- Speed is critical (0 hops = faster)
- Data is unstructured prose
Configure Graph Hops based on:
- Query complexity (simple = 0, complex = 2-3)
- Response time requirements
- Relationship depth in your data
What's Next
The knowledge graph needs data. The data comes from ETL pipelines that can automatically create new agents as they discover new domains.
Next up: Part 7 — ETL & Agent Creation, where we explore how SemanticStudio's self-learning ETL grows your multi-agent system.
Building SemanticStudio
Part 6 of 8